
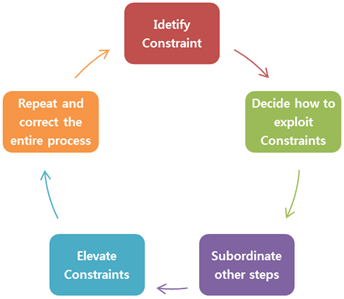
Dr Goldratt felt so strongly about this that he is quoted as saying: If this isn't done, it's likely that improvements to one part of the system will most likely make no difference to overall results, and it is even possible that an improvement to one part will make the overall result worse. One of the key principles of TOC is that you need to consider the entire system, not just one aspect, and identify the real constraint. Repeat the process to identify the next constraint.Alleviate the constraint by investing in additional resources and equipment.Subordinate and align all associated activities.Exploit the constraint with existing resources.To overcome this, Goldratt proposed five Theory of Constraints steps, known as the five focusing steps. In each case, unless the constraint is addressed, output is limited by that constraint. Typical Theory of Constraints examples would include: These constraints limit performance, and unless they are addressed, performance will not nor cannot improve. If this was not the case, there would be no limits and growth would be exponential. So, what is the Theory of Constraints? Goldratt proposed that every real system must have at least one if not more than one constraint preventing it from achieving better or higher levels of performance. In his book, a constraint was defined as anything that prevents the system from achieving its goal.
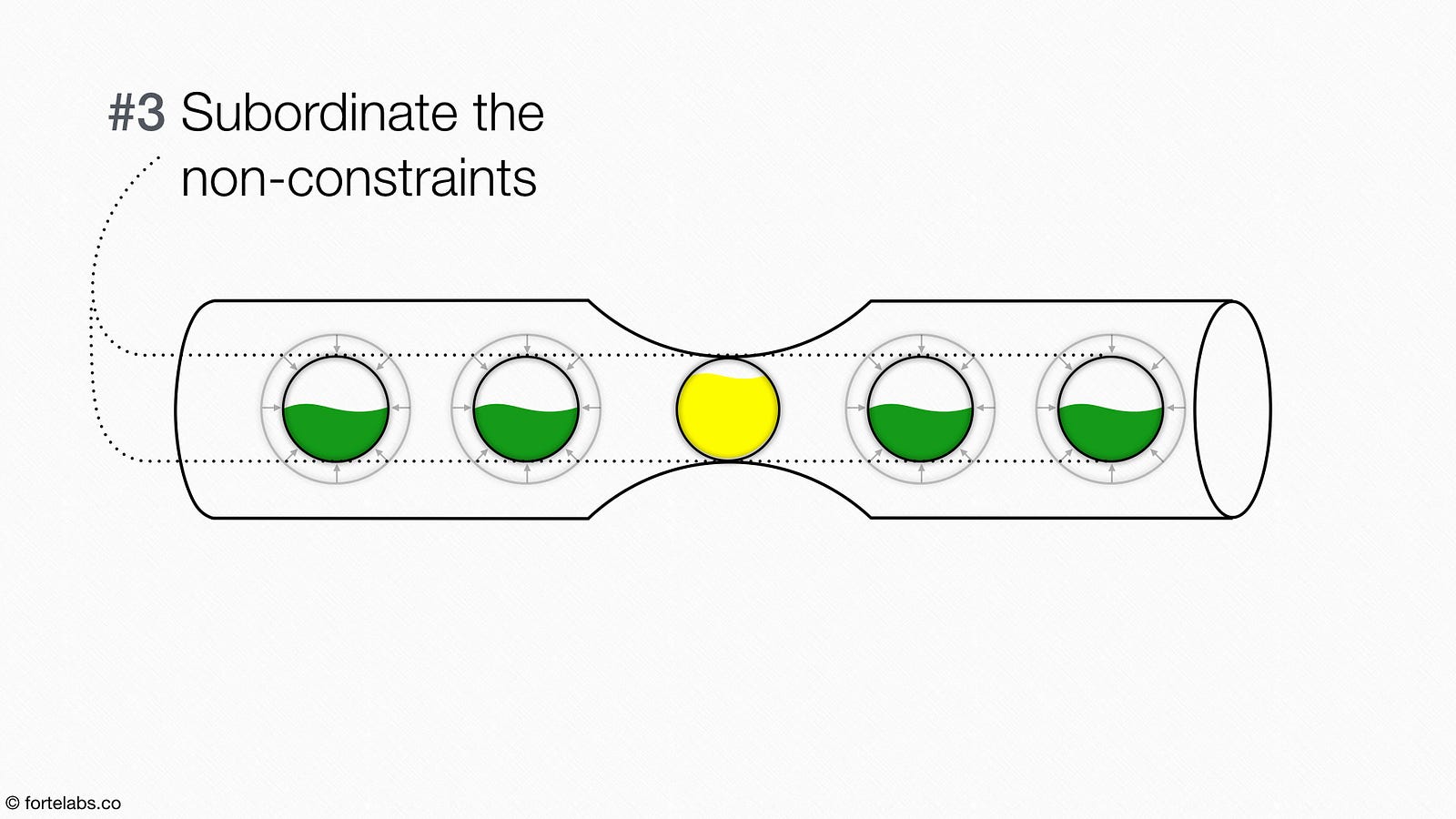
The key focus of the Theory of Constraints is identifying constraints or bottlenecks in any process, and working out how to eliminate or reduce their impact. This concept centers around practical methods for identifying solutions to business problems by deciding:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
